National Bureau of Economic Research
Latest from the NBER

Kosali Simon to Direct Program on the Economics of Aging
news article
Research Associate Kosali Simon, the Herman B. Wells Professor and Distinguished Professor at the Paul H. O'Neill School of Public and Environmental at Indiana University, will direct the NBER Program on the Economics of Aging at the start of the 2026–27 academic year. She succeeds Jonathan Skinner of Dartmouth College, who has directed the program since 2016. That was when David Wise of the Harvard Kennedy School, the program’s founding director, stepped down.
Simon, an NBER affiliate since 2002, has been an important contributor to the Aging Program, serving on the program's steering committee and co-organizing Summer Institute meetings…
A research summary from the monthly NBER Digest

Pass-Through of Tariffs: Evidence from European Wine Imports
article
The incidence of tariffs on producers, in the form of lower pre-tariff prices, and consumers, in the form of higher tariff-inclusive prices, is a long-standing issue in international economics. While economic theory suggests various possibilities, empirical evidence on the distribution of tariff burdens across the supply chain, from producers through distributors to retailers, is limited.
In Who Pays for Tariffs Along the Supply Chain? Evidence from European Wine Tariffs (NBER Working Paper 34392), Aaron B. Flaaen, Ali Hortaçsu, Felix Tintelnot, Nicolás Urdaneta, and Daniel Xu examine how tariff costs propagate through each stage of the wine distribution chain. The researchers...
From the NBER Bulletin on Health

Immunotherapy Increases the Cost of Cancer Care but Reduces Mortality
article
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) are immunotherapy drugs that mobilize the patient’s immune system to detect and attack cancer cells. They are considered a breakthrough development in cancer care, but are very expensive, with a full course of treatment costing more than $150,000 per patient. In The Impact of Immunotherapy on Reductions in Cancer Mortality: Evidence from Medicare (NBER Working Paper 34317), Danea Horn, Abby E. Alpert, Mark Duggan, and Mireille Jacobson use Medicare claims data to evaluate the impact of the first ICIs on healthcare use, costs, and mortality among beneficiaries diagnosed with...
From the NBER Reporter: Research, program, and conference summaries

Quantitative Trade Policy in a Changing World
article
Over the past three decades trade policy has profoundly shaped the structure of production, employment, and welfare across countries. The North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), China’s entry into the World Trade Organization (WTO), and the recent resurgence of tariff protectionism illustrate how deeply globalization and policy choices are intertwined. Evaluating their effects requires quantitative frameworks that capture how shocks to both technology and policy propagate through supply chains, labor markets, and international linkages.
Our research develops tractable general equilibrium models to quantify how shocks such as tariffs affect economies—both in the aggregate and across workers, regions, and sectors. These frameworks extend the Ricardian model of trade to include…
From the NBER Bulletin on Entrepreneurship
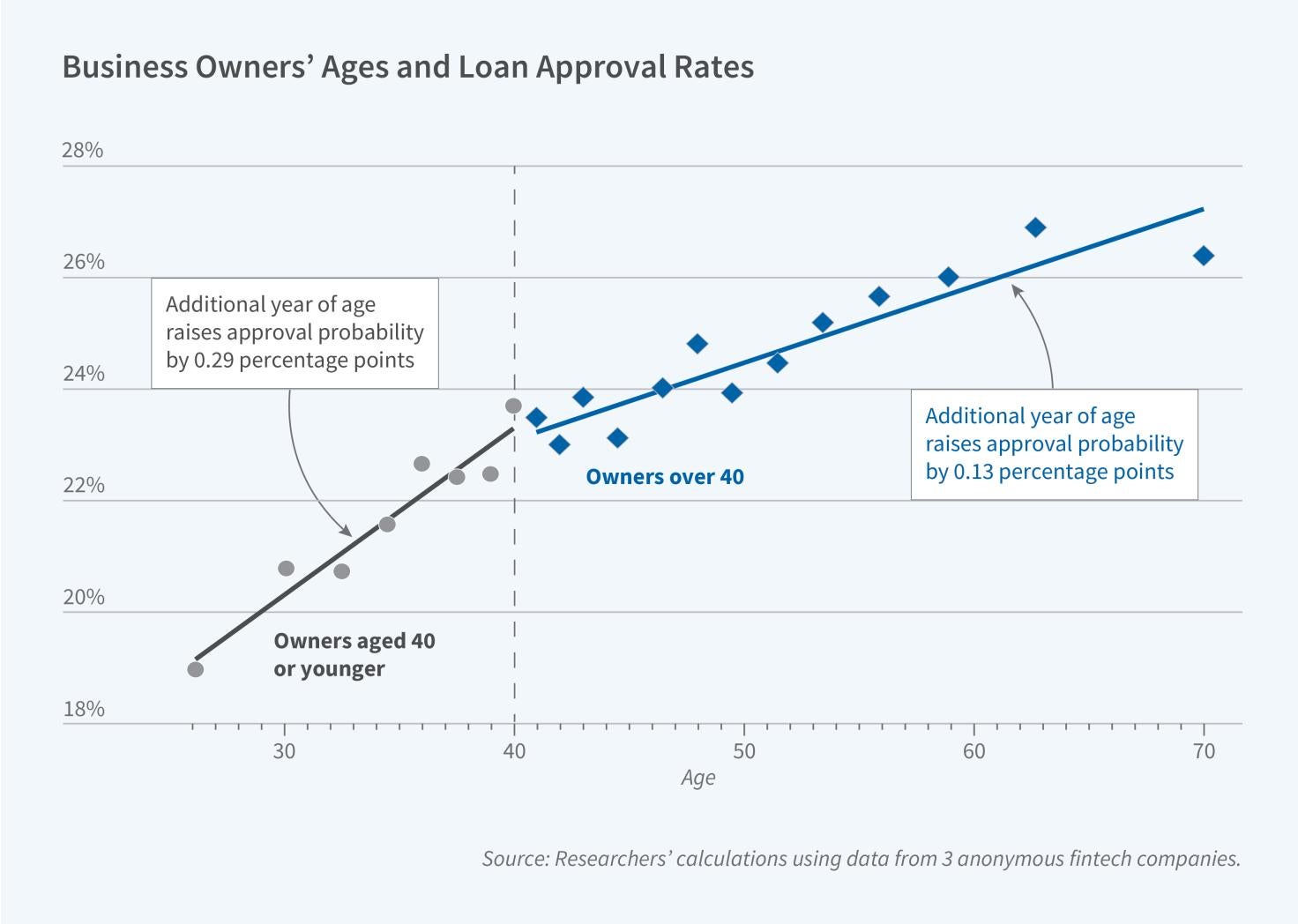
Underwriting Based on Cash Flow Helps Younger Entrepreneurs Access Credit
article
Younger entrepreneurs are disadvantaged in small business loan markets because lenders rely heavily on personal credit scores, which favor long histories of repaying debt. In Modernizing Access to Credit for Younger Entrepreneurs: From FICO to Cash Flow (NBER Working Paper 33367), researchers Christopher M. Hair, Sabrina T. Howell, Mark J. Johnson, and Siena Matsumoto document this fact and show that younger entrepreneurs benefit from underwriting that augments personal credit scores (like FICO) with cash flow data. They analyze comprehensive…
Featured Working Papers
Surveying US adults aged 60–74, Susann Rohwedder, Michael D. Hurd, and Axel H. Börsch-Supan find that saving regret is driven primarily by exposure to adverse economic shocks rather than procrastination, with 54 percent wishing they had saved more.
Bumsoo Kim, Marc De la Barrea, and Masao Fukui find that China's currency peg could account for 59 percent of the 793,000 US manufacturing jobs lost in the twelve years following China’s entry to the WTO in 2000.
Lenders who take longer to process loans also wait longer before selling them into securitization trusts. Both behaviors predict lower default rates, consistent with the anticipation of signaling quality through delayed sale encouraging more careful screening upfront, according to Manuel Adelino, Bin Wei, and Feng Zhao.
Decomposing real interest rate changes into three structural drivers—expected growth, risk, and "pure discounting"—Niels Joachim Gormsen and Eben Lazarus find that only the pure discounting component passes through to stock prices one-for-one. This component explains 80 percent of cross-country equity valuation changes across G7 nations since 1990.
Employees at firms founded after 2015 work from home (WFH) nearly twice as often as those at firms founded before 1990. WFH rates decline monotonically with CEO age, averaging 1.4 days per week under CEOs younger than 30 versus 1.1 days under CEOs 60 or older, according to Cevat Giray Aksoy, Jose Maria Barrero, Nicholas Bloom, Katelyn Cranney, Steven J. Davis, Mathias Dolls, and Pablo Zarate.
In the News
Recent citations of NBER research in the media
_______________________________________
Research Projects
Conferences
Books & Chapters
Through a partnership with the University of Chicago Press, the NBER publishes the proceedings of four annual conferences as well as other research studies associated with NBER-based research projects.
Videos
Recordings of presentations, keynote addresses, and panel discussions at NBER conferences are available on the Videos page.




