National Bureau of Economic Research
Latest from the NBER
From the NBER Bulletin on Health

Immunotherapy Increases the Cost of Cancer Care but Reduces Mortality
article
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) are immunotherapy drugs that mobilize the patient’s immune system to detect and attack cancer cells. They are considered a breakthrough development in cancer care, but are very expensive, with a full course of treatment costing more than $150,000 per patient. In The Impact of Immunotherapy on Reductions in Cancer Mortality: Evidence from Medicare (NBER Working Paper 34317), Danea Horn, Abby E. Alpert, Mark Duggan, and Mireille Jacobson use Medicare claims data to evaluate the impact of the first ICIs on healthcare use, costs, and mortality among beneficiaries diagnosed with...
A research summary from the monthly NBER Digest

Job Growth in Counties Targeted by the CHIPS and Science Act
article
The CHIPS and Science Act, passed in August 2022, committed the federal government to spending nearly $53 billion to revitalize domestic semiconductor production. While job creation was a central argument of the legislation's proponents, there has been limited assessment since its passage of whether the act delivered on employment promises. In Employment Impacts of the CHIPS Act (NBER Working Paper 34625), Bilge Erten, Joseph E. Stiglitz, and Eric Verhoogen use county-level data to provide empirical evidence on the short-term employment effects of this legislation.
The study applies two difference-in-differences research designs to data from the Quarterly Census of Employment...
New Initiative on Social Return to R&D Investment
news article
Investments in research, development, and innovation are widely recognized as key drivers of long-term economic growth but estimates of the social rate of return on these investments vary substantially. To encourage research on this topic, sometimes called "The Griliches Question," the NBER has launched a five-year project that will be organized around the creation of a pop-up journal devoted to this issue. The project will be led by NBER affiliates Craig Garthwaite (Northwestern University) and Timothy Simcoe (Boston University). A steering committee of leading scholars and policy experts will help guide the project, which will host an…
From the NBER Reporter: Research, program, and conference summaries

Quantitative Trade Policy in a Changing World
article
Over the past three decades trade policy has profoundly shaped the structure of production, employment, and welfare across countries. The North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), China’s entry into the World Trade Organization (WTO), and the recent resurgence of tariff protectionism illustrate how deeply globalization and policy choices are intertwined. Evaluating their effects requires quantitative frameworks that capture how shocks to both technology and policy propagate through supply chains, labor markets, and international linkages.
Our research develops tractable general equilibrium models to quantify how shocks such as tariffs affect economies—both in the aggregate and across workers, regions, and sectors. These frameworks extend the Ricardian model of trade to include…
From the NBER Bulletin on Entrepreneurship
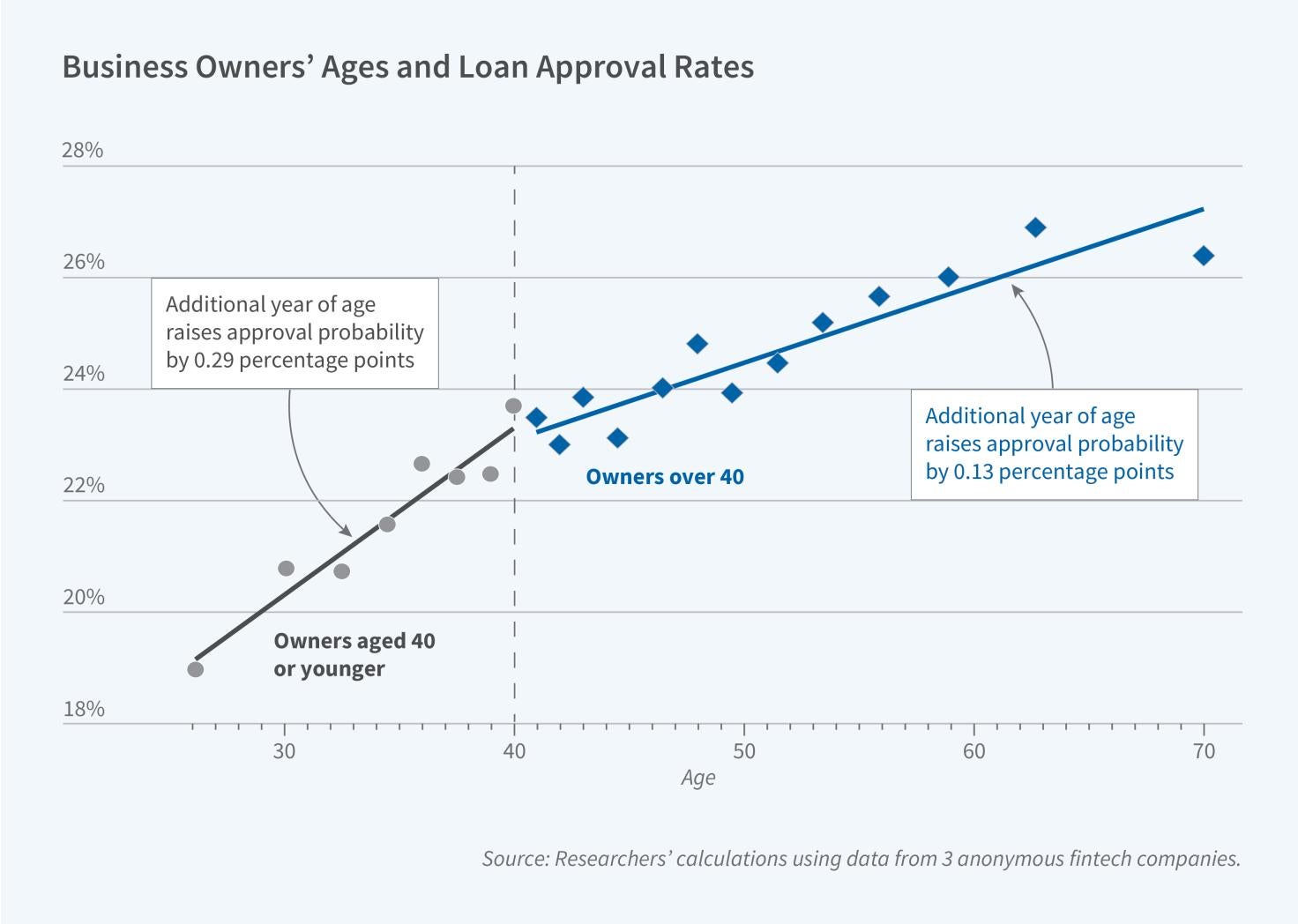
Underwriting Based on Cash Flow Helps Younger Entrepreneurs Access Credit
article
Younger entrepreneurs are disadvantaged in small business loan markets because lenders rely heavily on personal credit scores, which favor long histories of repaying debt. In Modernizing Access to Credit for Younger Entrepreneurs: From FICO to Cash Flow (NBER Working Paper 33367), researchers Christopher M. Hair, Sabrina T. Howell, Mark J. Johnson, and Siena Matsumoto document this fact and show that younger entrepreneurs benefit from underwriting that augments personal credit scores (like FICO) with cash flow data. They analyze comprehensive…
Featured Working Papers
While daily ICE arrests rose 170 percent following Trump's second inauguration, the share of those arrested with a criminal conviction declined from 52 percent to 37 percent, according to Chloe N. East, Caitlin Patler, and Elizabeth Cox.
Bruno Cavani, Christopher Clayton, Amanda Dos Santos, Matteo Maggiori, and Jesse Schreger find that US mutual fund holdings of Chinese Renminbi-denominated bonds fell roughly 50 percent between 2021 and 2024, with about 65 percent of the decline driven by funds exiting RMB positions entirely. At the same time, total foreign holdings of Chinese bonds rose to $625 billion in 2024.
David C. Grabowski, Jonathan Gruber, and Brian E. McGarry find that a 25 percent increase in the annual net flow of immigrants would result in roughly 5,000 fewer elderly deaths per year primarily because the immigrants expand the healthcare workforce and reduce nursing home use.
Over the 1988–2016 period, Nigeria increased intergovernmental VAT transfers to states that saw active protests and that were politically aligned with the federal government by up to 2.2 percent annually, while non-aligned states saw transfers fall and greater police violence in response to protests, Belinda Archibong, Chinemelu Okafor, Evans S. Osabuohien, and Tom Moerenhout find.
A 5-percentage point increase in a county’s exposure to the 1920s US immigration quota acts reduced the probability of upward occupational mobility for US-born white men in that county by roughly 1.9 percentage points, according to James J. Feigenbaum, Yi-Ju Hung, Marco Tabellini, and Monia Tomasella.
In the News
Recent citations of NBER research in the media
_______________________________________
Research Projects
Conferences
Books & Chapters
Through a partnership with the University of Chicago Press, the NBER publishes the proceedings of four annual conferences as well as other research studies associated with NBER-based research projects.
Videos
Recordings of presentations, keynote addresses, and panel discussions at NBER conferences are available on the Videos page.




