Co-Directors

Mark Aguiar is the Walker Professor of Economics and International Finance at Princeton University. His research spans both open- and closed-economy macroeconomics, including sovereign debt, business cycles in emerging markets, capital taxation, growth, and the micro-foundations of consumption and labor supply. He has been an NBER affiliate since 2008.

Linda Tesar is a professor of economics at the University of Michigan. Her research examines cross-country business cycle linkages, capital flows to emerging markets, the consequences of exchange rate exposure, and global risk-sharing. She has been an NBER affiliate since 1993.
Featured Program Content

Nearly a decade has passed since British voters narrowly chose to leave the European Union in June 2016. The referendum's outcome set in motion a complex...
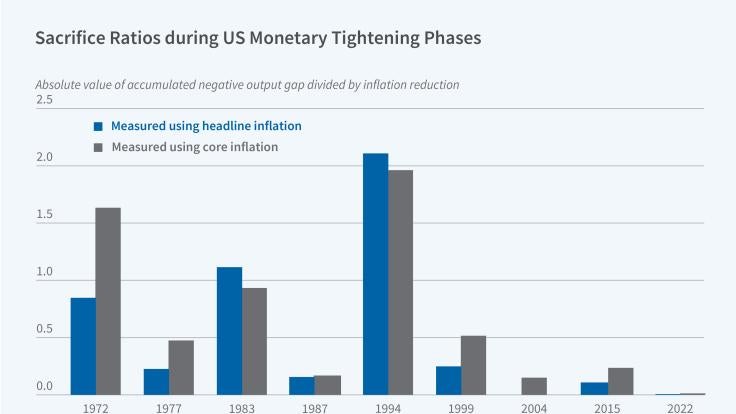
Central banks' decisions about when and how to adjust monetary policy require weighing multiple objectives. In Trade-offs over Rate Cycles: Activity,...
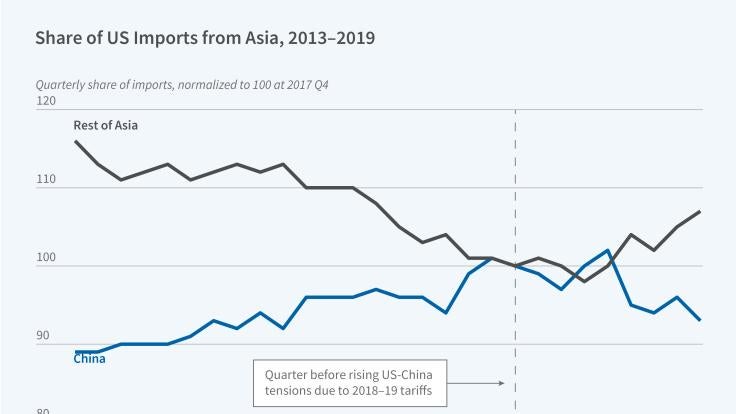
As US-China trade tensions escalated in 2018–19, American firms scrambled to reorganize their supply chains. In Bank Financing of Global Supply Chains (...